Updated 14 hours ago
Compared: Grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems
Written by
Zeeshan Hyder
There are three types of solar panel systems: grid-tied (on-grid), off-grid, and hybrid solar systems.
Each type of system has a unique setup that affects what equipment is used, the complexity of installation, and, most crucially, your potential costs and savings.
What would be the best in your situation? Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of different solar system types.
Grid-tied solar systems
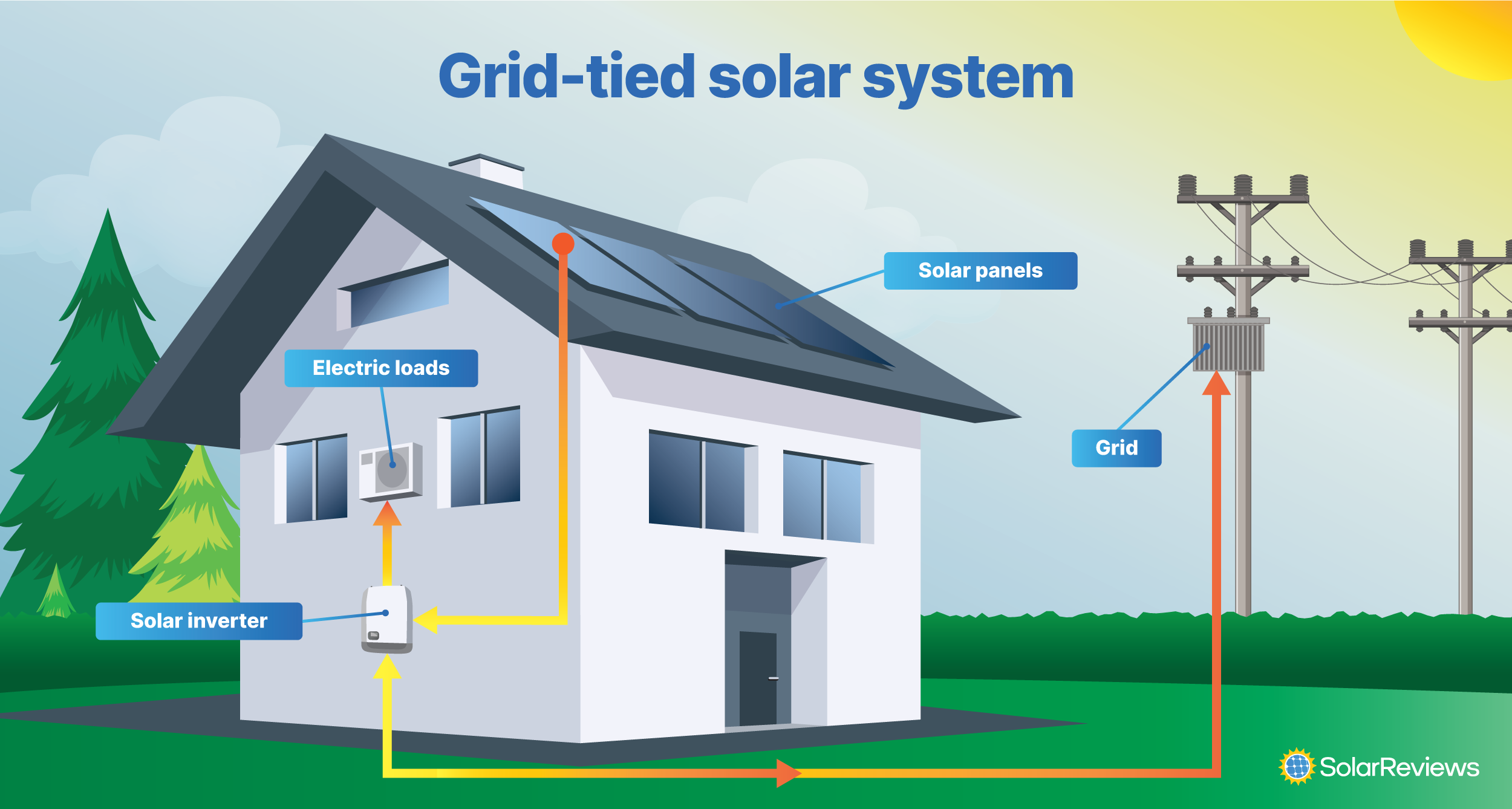
Grid-tied systems are solar panel installations that are connected to the utility power grid. With a grid-connected system, a home can use the solar energy produced by its solar panels and electricity that comes from the utility grid.
If the solar panels generate more electricity than a home needs, the excess is sent to the grid. In some places, a utility will purchase the solar energy sent to the grid in the form of a bill credit to offset future electricity costs thanks to a billing structure called net metering.
Grid-tied solar panel systems are so popular because they provide the best value for how much they cost, especially in areas with full-retail net metering. Their cost is low because they require less equipment than other solar system types. However, this also means grid-tied systems can’t keep your lights on when the power is out.
Pros
-
Cheapest home solar system
-
Less equipment
Cons
-
No backup power
Off-grid solar systems
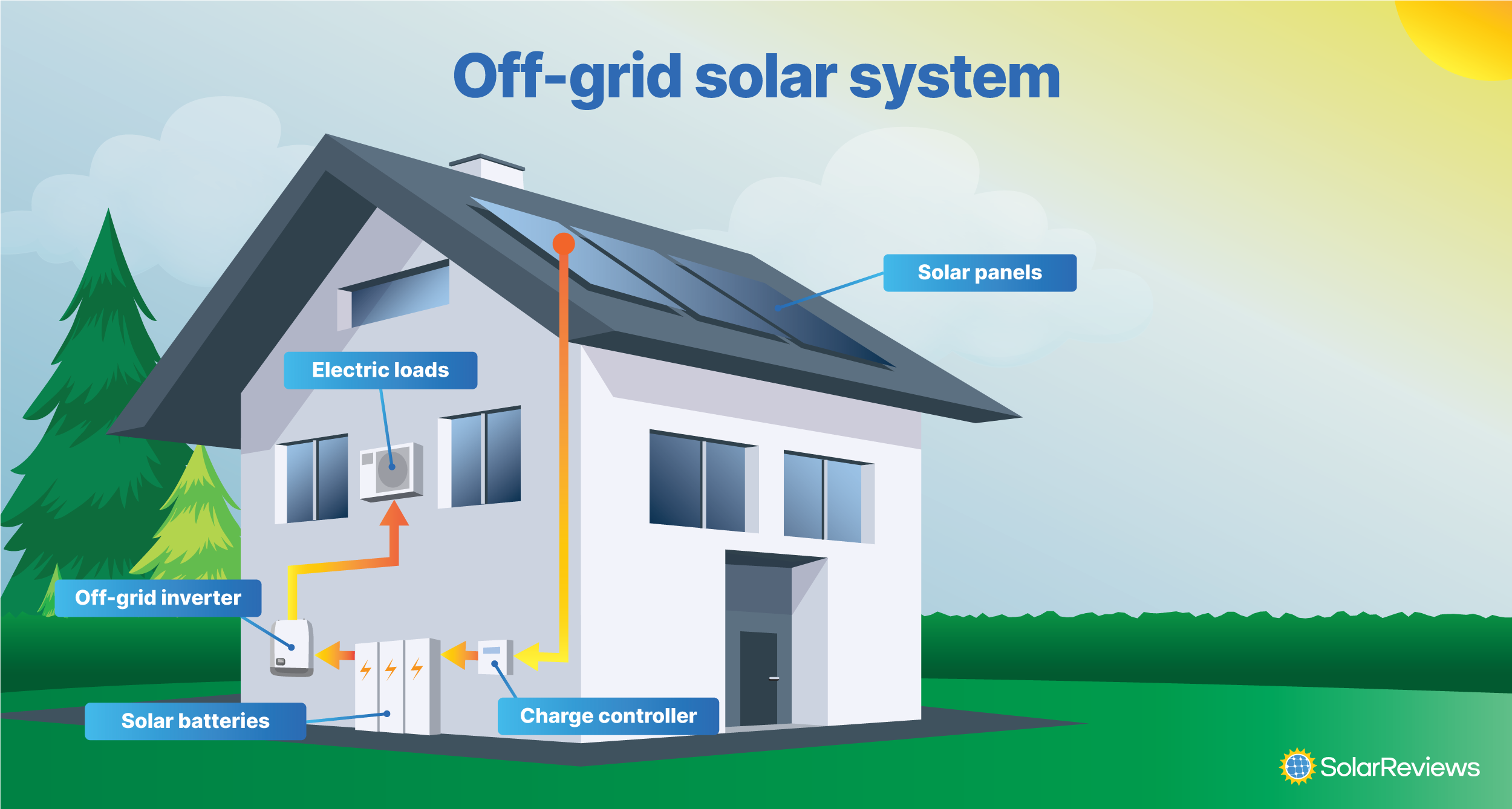
An off-grid solar system is a solar panel system that has no connection to the utility grid at all. To keep a house running off-grid, you need solar panels, a significant amount of battery storage, and usually another backup power source, like a gas-powered generator.
Sometimes called standalone systems, they’re common among homeowners who don’t have access to the grid, like in rural areas or remote cabins.
Believe it or not, there are plenty of places throughout the country that the utility grid doesn’t service. Off-grid systems give these remote areas access to electricity. Being off-grid also makes you more self-reliant; you’re not beholden to a utility company, and the power is in your hands.
But, off-grid systems are very expensive. You need a lot of battery storage to power an entire home without help from the grid, and the cost adds up. Going off-grid also requires certain lifestyle changes. You have to be very energy-conscious when you don’t have a grid with unlimited supply. Off-grid homeowners need to monitor their consumption and solar production to ensure they have the electricity needed.
Pros
-
Provides electricity where there is no grid access
-
Self-reliant
Cons
-
Very expensive
-
Requires lifestyle changes
Hybrid solar systems
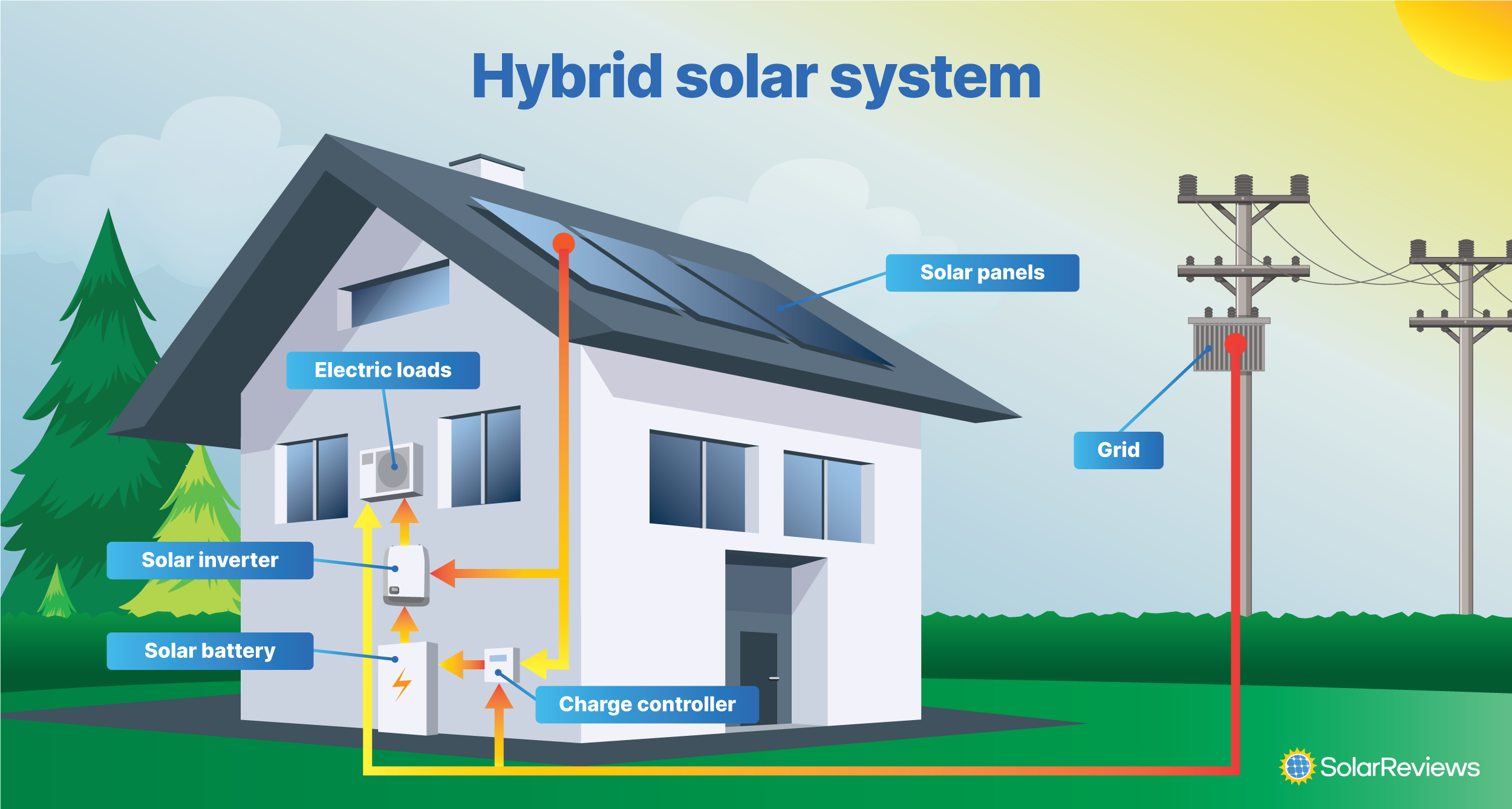
Hybrid solar systems combine the best of grid-tied and off-grid solar systems; the solar panels are attached to batteries and the utility grid. You’ll commonly see hybrid solar systems referred to as “solar-plus-storage” systems.
Solar-plus-storage systems are popular in areas that experience frequent grid failures or in places that don’t have full-retail net metering. Without a battery, solar panels can't run your home when the power goes out. Batteries also allow you to rely less on the grid by using stored energy when your solar panels aren’t producing electricity. This also maximizes the amount of clean energy your home uses!
Plus, batteries can even save a bit more money if you don't have access full retail net metering. However, the high upfront cost of batteries means they often don't pencil out financially.
Here are some of the pros and cons of installing a hybrid solar-plus-storage system
Pros
-
Provide backup power
-
Increase energy independence
-
Can potentially save more money on electricity bills
Cons
-
Expensive
-
Not always the right financial choice
How to pick the best solar system for you
A simple grid-tied system will usually be the best financial choice. Grid-tied systems generally provide the best return on investment because of their low upfront cost and simple system design.
However, there are some cases where a hybrid system may make the most sense for you, especially if you experience regular power outages. If you really value energy independence and maximizing the amount of renewable energy your home uses, then a solar plus storage system could be just what you’re looking for.
Off-grid systems are probably the least practical for everyday homeowners. But they are excellent for remote areas and may be the right choice for your mountain cabin.
The best way to figure out the right solar system for you is by contacting solar companies near you. Local solar installers will have the best understanding of the right solar system to install in your area and how you can get the most out of your solar panels.
Zeeshan is a solar journalist who has long been passionate about climate issues and developed a deep interest in solar power after witnessing its successful adoption in Australia. He has previously worked as a journalist for a major news organization, covering energy, climate, and environmental stories, among other topics. He also served as an organizer for the Pakistan Youth Climate Network, an advocacy group aimed at raising climate awareness...
Learn more about Zeeshan Hyder